APPENDIX K -- THE COMPOSTING HANDBOOK
SELECTED OSHA REGULATIONS PERTAINING TO COMPOSTING OPERATIONS
Compiled by Nellie Brown, Director of Workplace Health & Safety Programs
ILR School, Cornell University
Latest Revision: 12/01/2021
OSHA is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration of the U.S. government (https://www.osha.gov/ ). It is part of the U.S. Department of Labor. OSHA was created as part of the Occupational Health and Safety Act of 1970 “to ensure safe and healthful working conditions for workers by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education and assistance” (https://www.osha.gov/aboutosha). OSHA is the most influential organization guiding safe and health working conditions among private sector employers in the U.S. (an also those followed by the federal government). While individual states may establish their own safety and health rules and regulations, they typically follow OSHA’s lead and OSHA’s recommendations. Some states choose to cover public sector employees at the state, county, and municipal level; some states may choose to cover both public and private sector employees. Federal employees are covered by OSHA, but through Presidential Executive Orders which each President has chosen to continue to do.
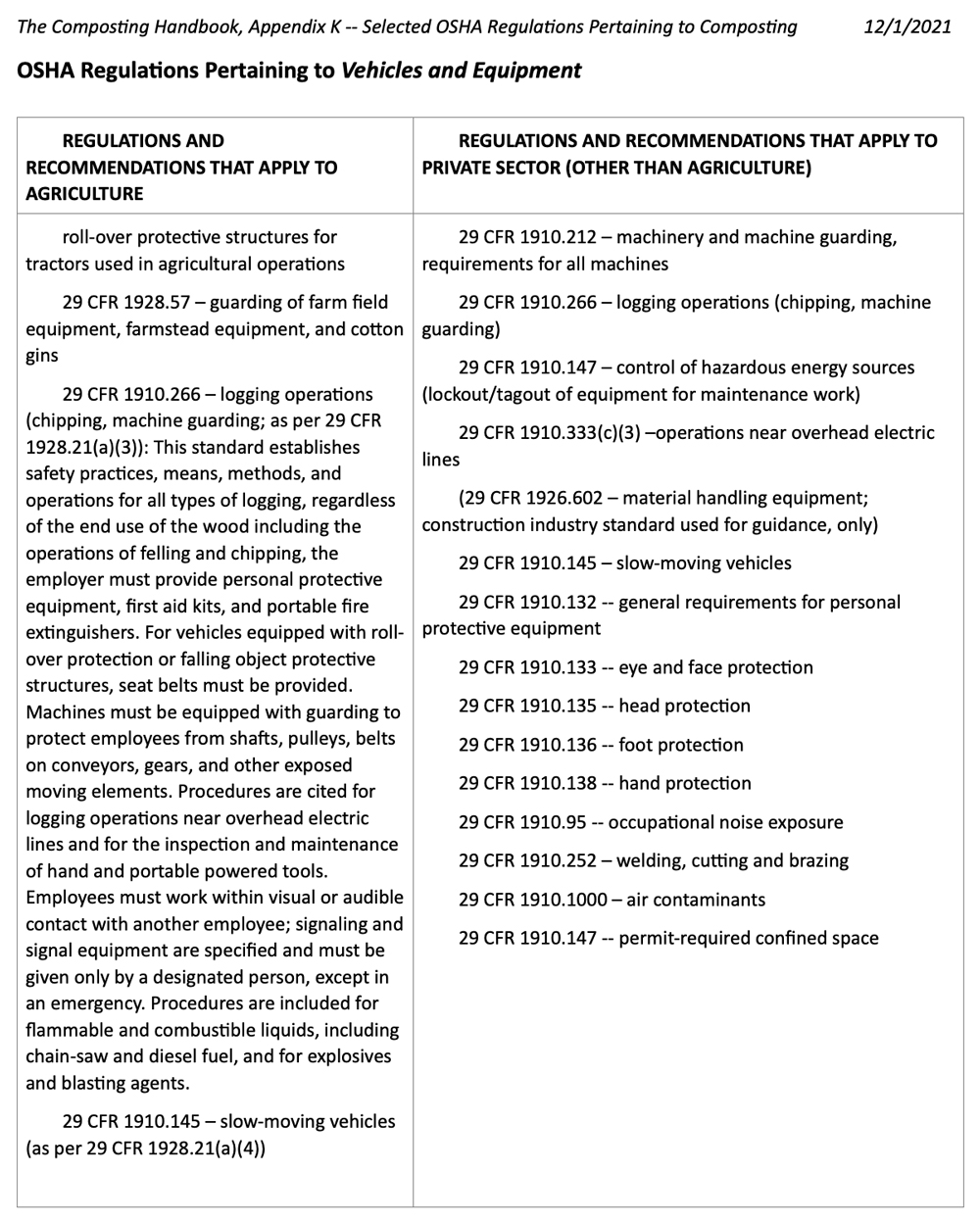
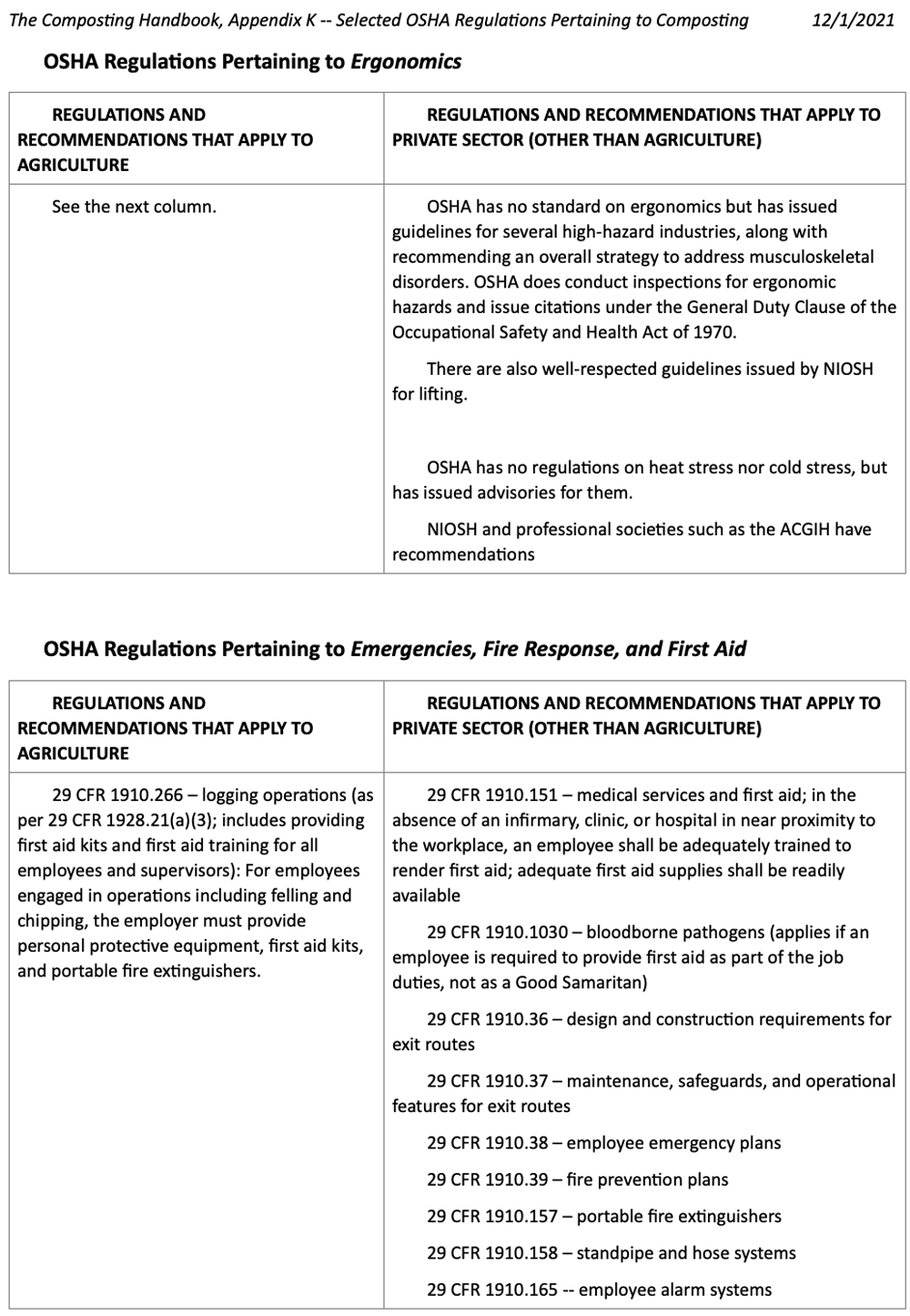
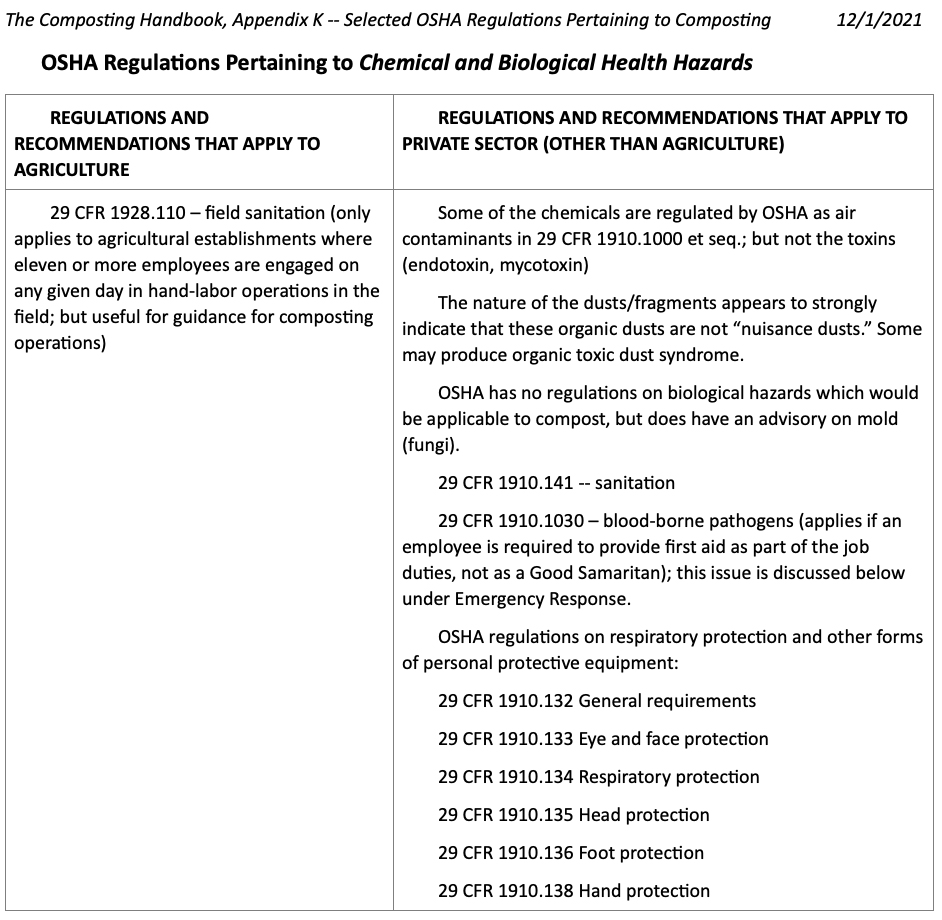
OSHA has many regulations, standards and recommendations covering a wide variety of labor activities and applications. The following regulations and recommendations are potentially, if not closely, related to safety and health at composting facilities. Details and commentary for each regulation/recommendation can be found by searching the OSHA “Laws and Regulations” web page (https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs) using the CFR number.
If a specific work activity or circumstance is not covered by an existing regulation, the General Duty Clause of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 applies (in fact, the general duty clause always applies). The general duty clause states (https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/oshact/section_5):
Each employer -- (1) shall furnish to each of his employees, employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees; and (2) shall comply with occupational safety and health standards promulgated under this Act.
Each employee shall comply with occupational safety and health standards and all rules, regulations, and orders issued pursuant to this Act which are applicable to his own actions and conduct.
In addition to OSHA, workplace health and safety guidance in the U.S. is provided by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), which is part of the U.S. government’s Centers for Disease Control and Prevention agency (https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/).